Intravenous Bacille Calmette–Guérin vaccination protects simian immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques from tuberculosis
2023.10.09.
Erica C. Larson et al, Nature Microbiology, 2023
ABSTRACT
Tuberculosis, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), is the most common cause of death in people living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Intra-dermal Bacille Calmette–Guérin (BCG) delivery is the only licensed vaccine against tuberculosis; however, it offers little protection from pulmonary tuberculosis in adults and is contraindicated in people living with HIV. Intravenous BCG confers protection against Mtb infection in rhesus macaques; we hypothesized that it might prevent tuberculosis in simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-infected macaques, a model for HIV infection. Here, intravenous BCG-elicited robust airway T cell influx and elevated plasma and airway antibody titers in both SIV-infected and naive animals. Following Mtb challenge, all 7 vaccinated SIV-naive and 9 out of 12 vaccinated SIV-infected animals were protected, without any culturable bacteria detected from tissues. Peripheral blood mononuclear cell responses post-challenge indicated early clearance of Mtb in vaccinated animals, regardless of SIV infection. These data support that intravenous BCG is immunogenic and efficacious in SIV-infected animals.
Results from MultiScan™ LFER PET/CT
- FDG imaging revealed substantial lung inflammation in both unvaccinated groups as early as 4 weeks post-Mtb challenge
- SIV-naive vaccinated animals displayed minimal lung inflammation over the 12 weeks of Mtb infection
- 3 of the 12 SIV+ vaccinated animals did have increased lung FDG activity
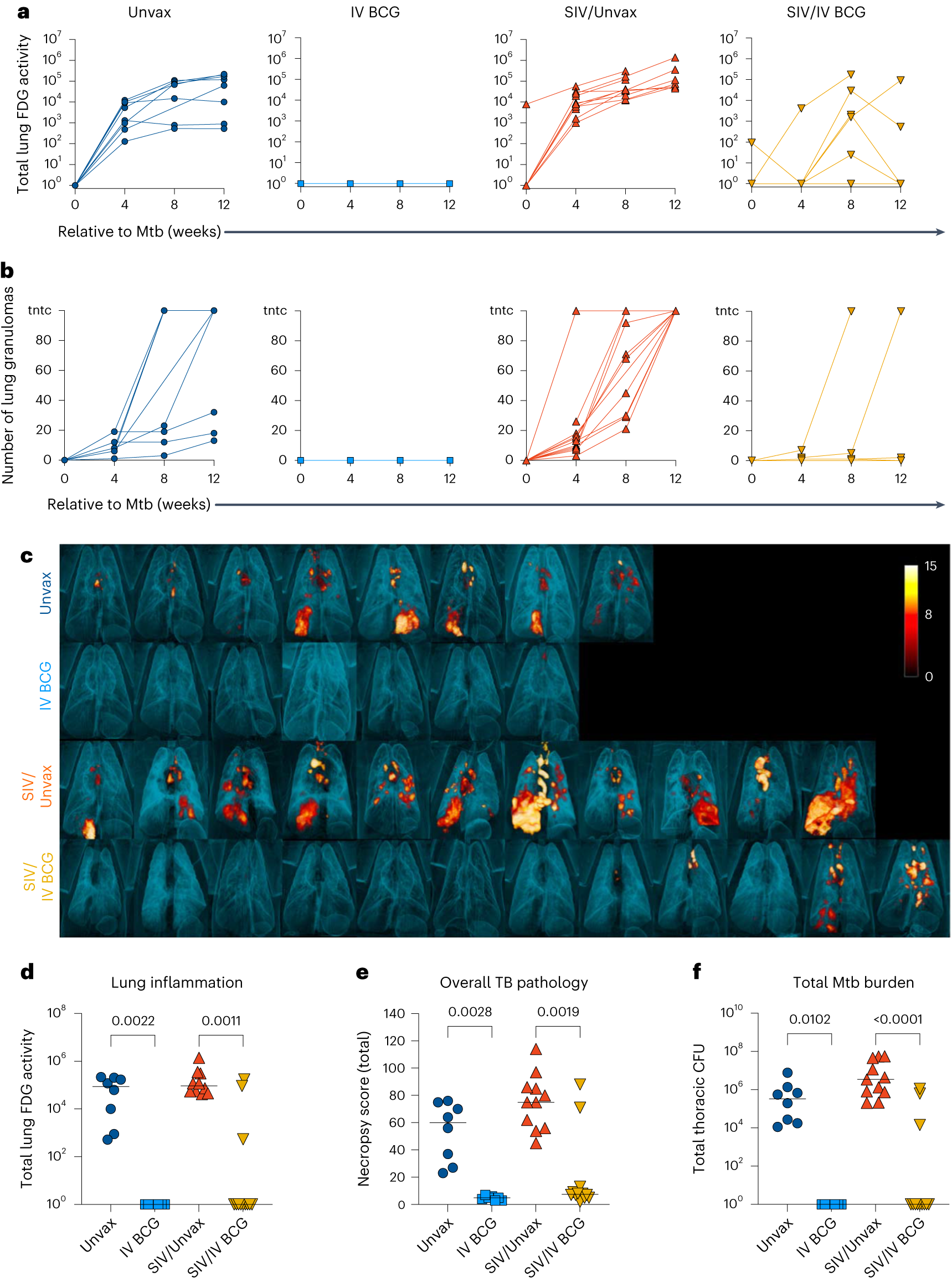
Fig. 6 a, Total FDG activity (lung inflammation) relative to Mtb challenge, measured by PET/CT imaging. Lines indicate individual animals. b, Number of lung granulomas relative to Mtb challenge. Animals with granuloma numbers >100 are indicated as too numerous to count (tntc). At 4 and 8 weeks, granulomas were counted by CT, whereas at 12 weeks, granulomas were counted by gross pathology. c, Three-dimensional renderings of PET/CT images of individual animals taken at necropsy. d–f, Lung inflammation (d), overall TB pathology (e) and total Mtb burden (thoracic CFU) (f) at necropsy. Each point indicates an individual animal and horizontal bars indicate group medians (Unvax, n = 8; IV BCG, n = 7; SIV/Unvax, n = 11; SIV/IV BCG, n = 12). Kruskal–Wallis tests were performed with Dunn’s multiple comparisons between SIV-naive, vaccinated and unvaccinated groups (dark-blue circles and light-blue squares, respectively), and SIV+, vaccinated and unvaccinated groups (red, up-pointing triangle and gold, down-pointing triangle, respectively). P values are shown. All statistical tests were two-sided.
W czym możemy pomóc?
Skontaktuj się z nami aby uzyskać informacje techniczne i / lub wsparcie dotyczące naszych produktów i usług.
Napisz do nas